Your cart is currently empty!

How to Treat Hyperpigmentation: An In-Depth Guide

Table of Contents
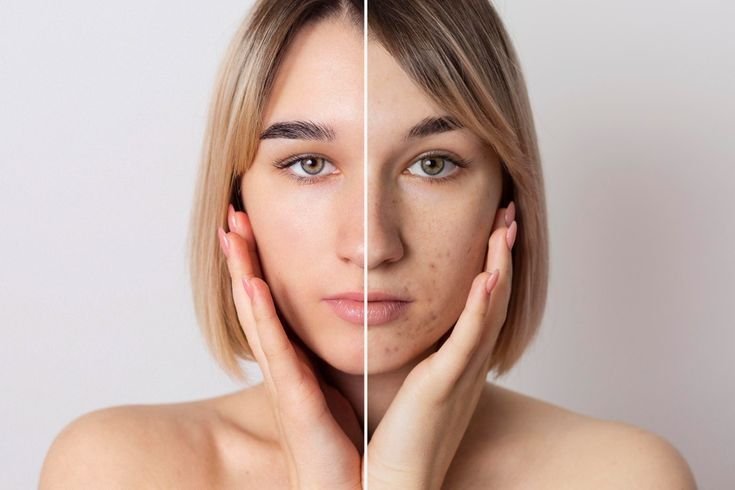
Hyperpigmentation, characterized by dark patches on the skin, is a common concern that can affect people of all skin types and ages. It occurs when an excess production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, forms deposits in the skin. This condition can be triggered by various factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, and certain medications. While hyperpigmentation is generally harmless, it can be aesthetically distressing, prompting many to seek effective treatment options.
Understanding the underlying causes of hyperpigmentation is crucial in devising a treatment plan. One of the primary culprits is sun exposure, which stimulates melanin production as a natural defense mechanism. Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy or from the use of birth control pills, can also lead to melasma, a form of hyperpigmentation. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation results from skin injury or inflammation, such as acne or eczema.
Effective treatments for hyperpigmentation include topical agents, medical procedures, and preventive measures. Topical treatments like hydroquinone, retinoids, and vitamin C can lighten dark spots over time. Medical procedures, such as chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion, offer more immediate results by targeting the deeper layers of the skin. Preventive strategies, including the use of broad-spectrum sunscreen and protective clothing, are essential to prevent further pigmentation.
1. Understanding Hyperpigmentation
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by the darkening of certain areas of the skin. This occurs when excess melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, forms deposits in the skin. Various factors can trigger hyperpigmentation, including sun exposure, inflammation, hormonal changes, certain medications, and skin injuries. Types of hyperpigmentation include age spots, melasma, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Although generally harmless, it can be aesthetically concerning for many people. Treatments often involve topical agents like hydroquinone, retinoids, or vitamin C, as well as procedures like chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion. Preventive measures include sun protection and skincare maintenance.
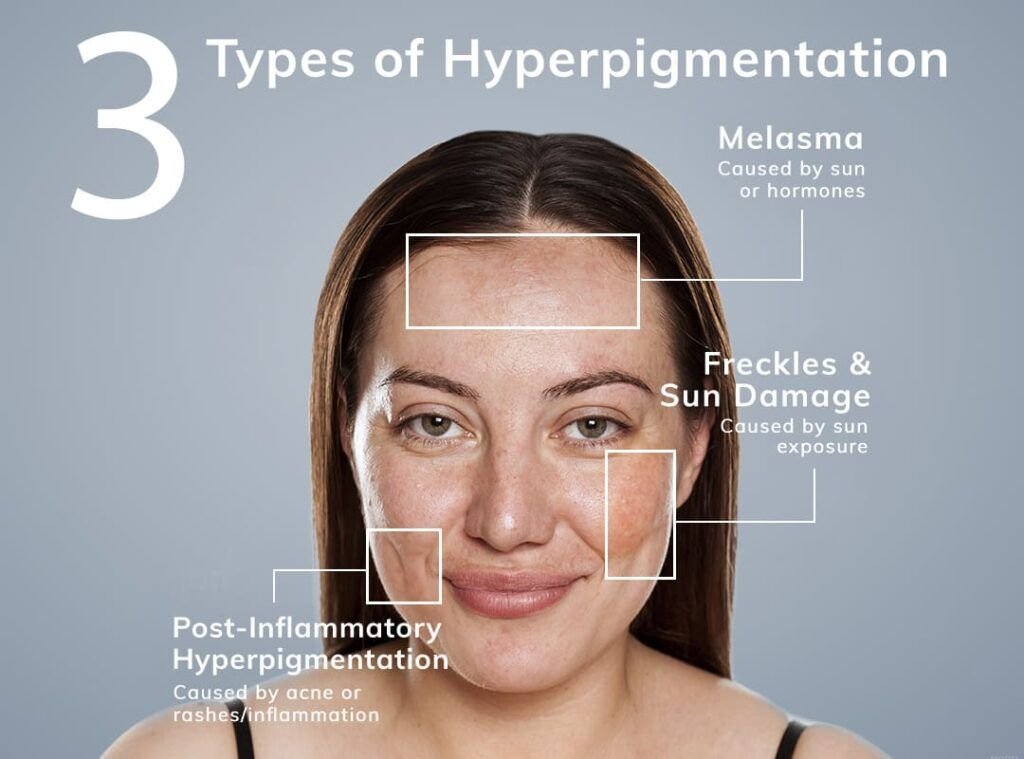
Types of Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by darkened areas on the skin. The three main types are:
- Melasma: Often caused by hormonal changes, melasma presents as brown or gray-brown patches, typically on the face. It is common during pregnancy or with oral contraceptive use.
- Sunspots: Also known as solar lentigines or age spots, these appear due to prolonged sun exposure. They are usually found on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, and arms.
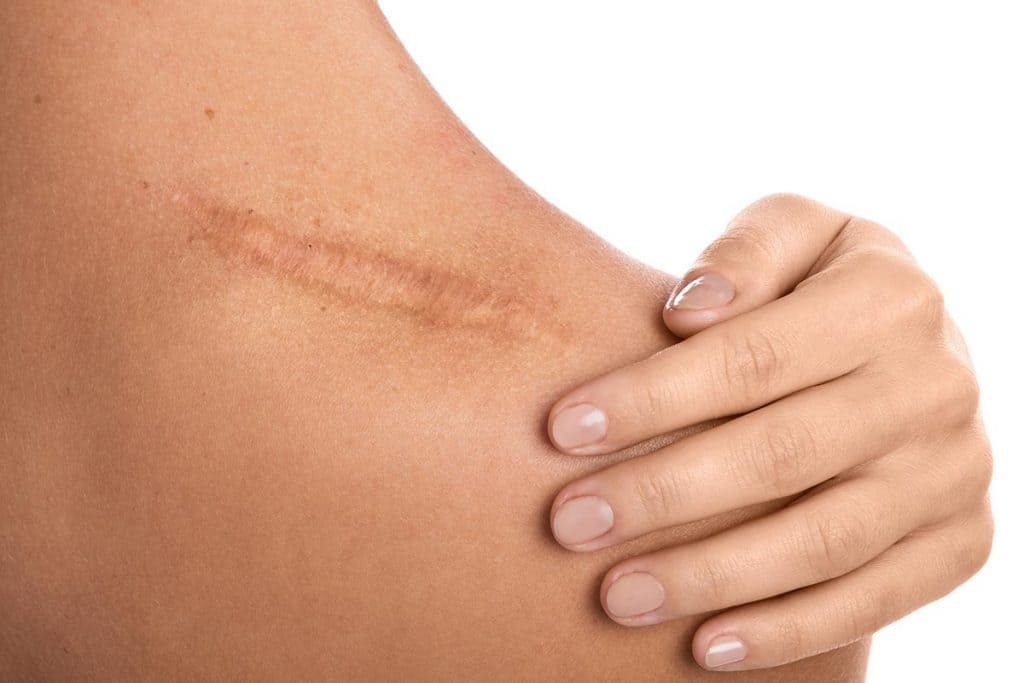
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): This type occurs after skin injury or inflammation, such as acne, cuts, or burns, leaving dark spots as the skin heals.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation occurs when the skin produces excess melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Common causes include sun exposure, which triggers melanin production to protect the skin from UV rays, and inflammation due to acne, eczema, or injuries that lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Hormonal changes, such as those during pregnancy or from birth control pills, can also cause melasma, a type of hyperpigmentation. Additionally, certain medications and medical conditions, such as Addison’s disease, can result in increased melanin production. Genetics and age are other factors, as skin naturally develops age spots over time.
2. Preventing Hyperpigmentation
Preventing hyperpigmentation involves a combination of daily habits and skincare practices. Always use broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 to protect your skin from UV damage. Incorporate antioxidants like Vitamin C into your skincare routine to fight free radicals and brighten your complexion. Exfoliate regularly to remove dead skin cells and promote cell turnover, but avoid over-exfoliation. Maintain a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals, and stay hydrated to support overall skin health. Lastly, avoid picking or squeezing pimples to prevent dark spots from forming due to inflammation and scarring.
Daily Sun Protection
Daily sun protection is essential for maintaining healthy skin and preventing premature aging and skin cancer. Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every morning, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating. Complement sunscreen with protective clothing, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses. Seek shade during peak sun hours, typically from 10 AM to 4 PM. Incorporate antioxidants like Vitamin C into your skincare routine to boost protection against UV damage. Consistent sun protection helps preserve your skin’s youthful appearance and reduces the risk of long-term damage.
Avoiding Skin Trauma
Avoiding skin trauma is crucial for maintaining healthy, glowing skin. To prevent damage, always handle your skin gently. Use lukewarm water for cleansing, as hot water can strip natural oils. Choose mild, fragrance-free cleansers and avoid harsh scrubbing. When drying your face, pat gently with a soft towel instead of rubbing. Incorporate a broad-spectrum sunscreen into your daily routine to protect against UV rays. Moisturize regularly to keep your skin hydrated and resilient. Avoid picking or squeezing blemishes to prevent scarring and infection. Lastly, manage stress and maintain a balanced diet to support overall skin health.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle involves a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and managing stress. Eating a variety of nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, is crucial. Engaging in physical activity for at least 30 minutes most days improves cardiovascular health and boosts mood. Quality sleep supports overall well-being and allows the body to repair itself. Managing stress through relaxation techniques or hobbies promotes mental health. Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption is also important. These habits work synergistically to enhance longevity and quality of life.

3. Topical Treatments for Hyperpigmentation
Topical treatments for hyperpigmentation can help even out skin tone and fade dark spots. Ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, and retinoids are commonly used to lighten pigmentation. Vitamin C serums and niacinamide can also brighten skin and reduce discoloration. Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) exfoliate the skin, promoting cell turnover and fading pigmented areas. Sunscreen is crucial to prevent further darkening of spots. Always consult a dermatologist before starting any treatment, as they can recommend the best products and formulations for your skin type and condition. Consistency and patience are key, as results may take several weeks to months to become noticeable.
Over-the-Counter Products
Many effective treatments are available without a prescription:
- Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent that can reduce the appearance of dark spots.
- Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives that promote cell turnover and improve skin texture.
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): These exfoliants help remove dead skin cells and improve the appearance of dark spots.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that brightens skin and inhibits melanin production.
- Niacinamide: A form of vitamin B3 that can lighten dark spots and improve skin barrier function.
Prescription Treatments
For more severe hyperpigmentation, a dermatologist may recommend prescription treatments:
- Tretinoin: A potent retinoid that increases cell turnover and fades dark spots.
- Corticosteroids: These can reduce inflammation and lighten hyperpigmented areas.
- Azelaic Acid: This acid helps to reduce inflammation and pigmentation.
- Tranexamic Acid: Used to treat melasma, this acid can lighten dark spots and improve skin tone.
Natural Remedies
Some people prefer natural treatments for hyperpigmentation:
- Aloe Vera: Contains aloin, which can lighten dark spots.
- Green Tea Extract: An antioxidant that can reduce melanin production.
- Licorice Extract: Contains glabridin, which has skin-lightening properties.
- Mulberry Extract: Reduces tyrosinase activity, an enzyme involved in melanin production.
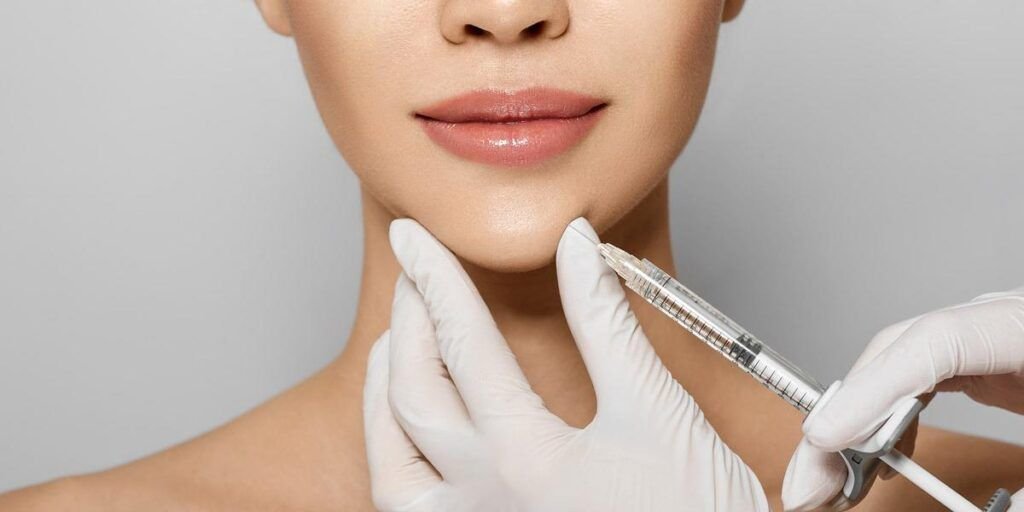
4. Professional Treatments for Hyperpigmentation
Professional treatments for hyperpigmentation include chemical peels, laser therapy, microdermabrasion, and prescription medications. Chemical peels use acids to exfoliate the outer layer of skin, revealing a smoother, more even complexion. Laser therapy targets pigmented areas with high-intensity light, breaking down excess melanin. Microdermabrasion gently exfoliates the skin, reducing the appearance of dark spots. Prescription medications like hydroquinone, retinoids, and corticosteroids can also be effective in treating hyperpigmentation. It’s essential to consult with a dermatologist to determine the best treatment plan for your skin type and condition. Regular sunscreen use and a gentle skincare routine can also help prevent further hyperpigmentation.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a solution to the skin that causes it to exfoliate and eventually peel off, revealing new, lighter skin underneath. Types of chemical peels include:
- Superficial Peels: Use mild acids like alpha-hydroxy acid to gently exfoliate.
- Medium Peels: Use stronger acids like glycolic or trichloroacetic acid to penetrate the middle layer of skin.
- Deep Peels: Use potent acids like phenol to deeply penetrate the skin.
Laser Therapy
Laser treatments can target hyperpigmented areas with precision:
- Ablative Lasers: Remove the top layer of skin, promoting new skin growth.
- Non-Ablative Lasers: Stimulate collagen production without removing the top layer of skin.
- Fractional Lasers: Target small areas of skin, promoting healing and new skin growth.
5. Diet and Supplements for Hyperpigmentation
To address hyperpigmentation, a diet rich in antioxidants and vitamins is key. Include foods like berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits for their vitamin C content, which can help brighten skin. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish or supplements can reduce inflammation and improve skin texture. Zinc-rich foods like nuts and seeds aid in skin repair. Additionally, consider supplements like vitamin C, E, and niacinamide, which are known to promote even skin tone. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure they are suitable for you. Combining these dietary changes with a good skincare routine can help manage hyperpigmentation effectively.
Foods That Help
Certain foods can support skin health and reduce hyperpigmentation:
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Berries, nuts, and green leafy vegetables can protect your skin from damage.
- Vitamin C: Citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers can boost collagen production and reduce melanin.
- Vitamin E: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and spinach can protect skin from UV damage.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts can reduce inflammation.
Supplements for Skin Health
If your diet lacks certain nutrients, supplements can help:
- Vitamin C: Helps to brighten skin and reduce pigmentation.
- Vitamin E: Protects against UV damage.
- Zinc: Supports skin repair and reduces inflammation.
- Glutathione: An antioxidant that can lighten skin.
6. Skincare Routine for Hyperpigmentation
A targeted skincare routine for hyperpigmentation involves gentle cleansing to remove impurities without stripping the skin, followed by exfoliation with AHAs or BHAs to encourage cell turnover. Incorporating a vitamin C serum can help brighten and even out skin tone, while niacinamide can reduce the appearance of dark spots. Using a moisturizer with SPF during the day helps protect against further pigmentation, and applying a retinoid at night can promote skin renewal. Consistency is key, and it’s advisable to patch-test new products and consult with a dermatologist for personalized advice.
Cleansing
A gentle cleanser effectively removes impurities without stripping the skin’s natural oils. Look for a formula with hydrating ingredients like hyaluronic acid and glycerin to maintain moisture balance. Avoid harsh chemicals like sulfates and alcohol, which can dry out the skin. Opt for a pH-balanced cleanser to keep the skin’s protective barrier intact. Massage the cleanser onto damp skin in circular motions, then rinse thoroughly with lukewarm water. Pat the skin dry with a soft towel and follow up with a moisturizer to lock in hydration. This ensures a clean, refreshed complexion without compromising skin health.
Exfoliating
Exfoliating is a crucial step in any skincare routine, helping to remove dead skin cells and reveal smoother, brighter skin. It can be done using physical exfoliants like scrubs or chemical exfoliants like AHAs and BHAs. Regular exfoliation can improve skin texture, reduce the appearance of pores, and enhance the effectiveness of other skincare products. However, it’s important not to overdo it, as excessive exfoliation can damage the skin’s barrier and lead to irritation. It’s best to exfoliate 1-3 times a week, depending on your skin type, to maintain a healthy and glowing complexion.
Moisturizing
Moisturizing is essential for maintaining healthy skin, especially in summer. It helps to hydrate the skin, keeping it soft and supple. Using a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer is ideal, as it won’t clog pores. Look for ingredients like hyaluronic acid or glycerin, which draw moisture into the skin. Apply moisturizer after cleansing and toning, and before sunscreen in the morning. In the evening, use a richer moisturizer to repair and nourish the skin while you sleep. Consistent moisturizing can improve skin texture, reduce the appearance of fine lines, and promote a radiant complexion, making it a crucial step in any skincare routine.
Targeted Treatments
To treat hyperpigmentation effectively, incorporate serums or treatments specifically formulated for this purpose into your skincare routine. Look for products containing ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, kojic acid, or alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) such as glycolic acid. These ingredients can help lighten dark spots and even out skin tone over time. Apply the serum or treatment to cleansed skin, focusing on areas with hyperpigmentation, and follow up with a moisturizer and sunscreen during the day. Consistent use, along with sun protection, can help fade hyperpigmentation and promote a more even complexion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, treating hyperpigmentation requires a multifaceted approach tailored to individual skin types and concerns. Consistency is key, whether using topical treatments, undergoing procedures, or incorporating lifestyle changes. Sun protection is non-negotiable, as UV exposure can worsen pigmentation. Patience is crucial, as results may take weeks or months to manifest. Consulting a dermatologist is advised for personalized treatment plans and to address any underlying medical conditions. With the right regimen and care, achieving a more even skin tone is possible. Embrace your journey to healthier, radiant skin!













Leave a Reply